Domain Name System Definition And Example. DNS is a directory service that provides a mapping between the name of a host on the network and its numerical address. The Domain Name System DNS converts a domain name into its specific IP address that computer want to communicate.
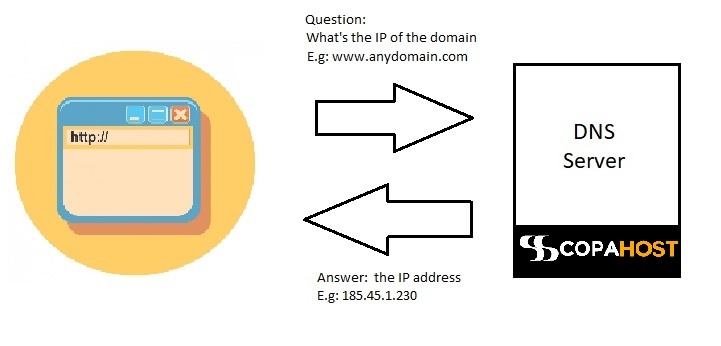
DNS stands for Domain Name System. The DNS can be quickly and transparently updated allowing a services location on the network to change without affecting the end users who continue to use the same hostname. In simple terms a Domain Name System DNS is a collection of databases that translate hostnames to IP addresses.
It associates various information with domain names assigned to each of the participating entities.
When a user enters your domain name into a web browser the browser uses your domain name to search and identify the correct IP address and as a result passes the website associated with that IP address. In 2017 3306 million domain names had been registered. Domain names are used to identify one or more IP addresses. When a user enters your domain name into a web browser the browser uses your domain name to search and identify the correct IP address and as a result passes the website associated with that IP address.